15 KiB
| sub_title | auther | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Time Systems 10 |
|
Week 1.3
assignment 3.1
Base your code of
opdr_2_1.zip.
Configure theSysTicktimer to set theCOUNTFLAGin theSTK_CTRLregister every0.5s. Replace the for-loop with the following C code:while (( STK_CTRL & (1 << 16)) == 0);You have to properly define the symbol STK_CTRL yourself to make this work. Build and debug the project. If all is well, the user LEDs will blink with a frequency of1 Hz.
With bit 2 of STK_CTRL the clock source can be set. 1 for AHB or 0 for AHB/8. AHB is by default HSI witch is 16MHz. I chose to use AHB/8.
T = \frac{AHB/8}{f_{out}} = \frac{16\cdot 10^6/8}{2} = 10^6
My resulting code:
#include <stdint.h>
#define RCC_AHB1ENR_BIT_GPIODEN *(volatile uint32_t*)(0x42000000 + 0x00023830 * 32 + 3 * 4)
#define GPIOD_BASE 0x40020C00
#define GPIOD_MODER *(volatile uint32_t*)(GPIOD_BASE + 0x00)
#define GPIOD_ODR *(volatile uint32_t*)(GPIOD_BASE + 0x14)
#define STK_CTRL *(volatile uint32_t*)(0xE000E010)
#define STK_LOAD *(volatile uint32_t*)(0xE000E014)
int main(void)
{
// GPIO Port D Clock Enable
RCC_AHB1ENR_BIT_GPIODEN = 1;
// GPIO Port D Pin 15 down to 12 Push/Pull Output
GPIOD_MODER = 0x55000000;
// Set green and red LEDs
GPIOD_ODR = 0x5000;
// SysTick enable with clk source to AHB/8
// (AHB is by default HSI; 16 MHz/8)
STK_CTRL = 1;
STK_LOAD = 1000000; // 16 MHz / 8 / 2 Hz
// Do forever:
while (1)
{
// Wait a moment
while ((STK_CTRL & (1 << 16)) == 0);
// Flip all LEDs
GPIOD_ODR ^= 0xF000;
}
}
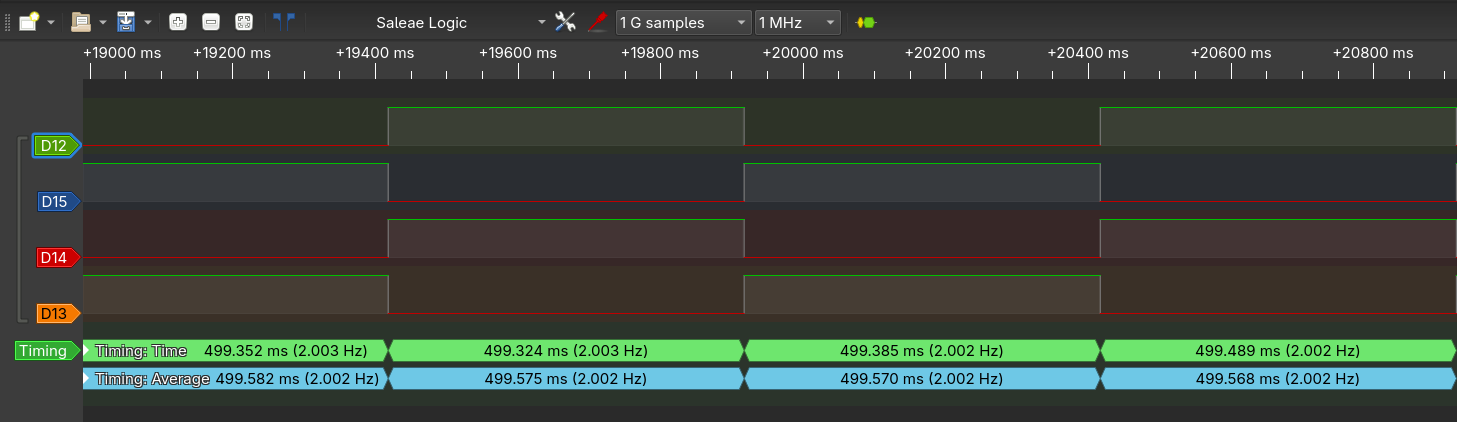
I measured the resulting frequency with an logic analyser (#logic-analiser-view-of-LEDs-for-assignment-31; channels are collerd to the led color). It measuerd a period time of 499.568ms, I call this error could be my cheap logic analyser or en error in the internal oscilator.
assignment 3.2
Configure the SysTick timer to set the
COUNTFLAGin theSTK_CTRLregister every0.5susing the CMSIS API. Replace the for-loop with the following C code:while ((SysTick->CTRL & (1 << 16)) == 0);The symbol SysTick is defined in the CMSIS API. Build and debug the project. If all is well, the user LEDs will blink with a frequency of1 Hz.
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stm32f4xx.h>
int main(void)
{
// GPIO Port D Clock Enable
RCC->AHB1ENR = RCC_AHB1ENR_GPIODEN;
// GPIO Port D Pin 15 down to 12 Push/Pull Output
GPIOD->MODER = GPIO_MODER_MODER12_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER13_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER14_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER15_0;
// Set green and red LEDs
GPIOD->ODR = GPIO_ODR_OD12 | GPIO_ODR_OD14;
// SysTick enable with clk source to AHB/8
SysTick->CTRL = SysTick_CTRL_ENABLE_Msk;
SysTick->LOAD = 1000000; // 16 MHz / 8 / 2 Hz
// Do forever:
while (1)
{
// Wait a moment
while ((SysTick->CTRL & (1 << 16)) == 0);
// Flip all LEDs
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD12
| GPIO_ODR_OD13
| GPIO_ODR_OD14
| GPIO_ODR_OD15;
}
}
This time I measured 499.586ms with the logic analyser.
assignment 3.3
B) Configure the SysTick timer to generate an interrupt (also called an exception) every
0.5s.
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define RCC_AHB1ENR_BIT_GPIODEN *(volatile uint32_t*)(0x42000000 + 0x00023830 * 32 + 3 * 4)
#define GPIOD_BASE 0x40020C00
#define GPIOD_MODER *(volatile uint32_t*)(GPIOD_BASE + 0x00)
#define GPIOD_ODR *(volatile uint32_t*)(GPIOD_BASE + 0x14)
#define STK_CTRL *(volatile uint32_t*)(0xE000E010)
#define STK_LOAD *(volatile uint32_t*)(0xE000E014)
volatile bool flag = false;
void SysTick_Handler()
{
flag = true;
}
int main(void)
{
// GPIO Port D Clock Enable
RCC_AHB1ENR_BIT_GPIODEN = 1;
// GPIO Port D Pin 15 down to 12 Push/Pull Output
GPIOD_MODER = 0x55000000;
// Set green and red LEDs
GPIOD_ODR = 0x5000;
// SysTick enable with interupt and clk source to AHB/8
STK_CTRL = (1<<1) | 1;
STK_LOAD = 1000000; // 0.5 sec / (16 MHz / 8)
// Do forever:
while (1)
{
// Wait a moment
while (!flag)
{
__asm__(" WFI"); // sleep until SysTick
}
flag = false;
// Flip all LEDs
GPIOD_ODR ^= 0xF000;
}
}
C) Why must the flag variable be defined as volatile?
becouse the compiler doesn't know when flag changes. Without volatile optimisations can think it does not change at all.
assignment 3.4
Configure the SysTick timer to generate an interrupt every
0.5s. This can be done by using the functionSysTick_Configfrom the CMSIS API.
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stm32f4xx.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
volatile bool flag = false;
void SysTick_Handler()
{
flag = true;
}
int main(void)
{
// GPIO Port D Clock Enable
RCC->AHB1ENR = RCC_AHB1ENR_GPIODEN;
// GPIO Port D Pin 15 down to 12 Push/Pull Output
GPIOD->MODER = GPIO_MODER_MODER12_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER13_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER14_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER15_0;
// Set green and red LEDs
GPIOD->ODR = GPIO_ODR_OD12 | GPIO_ODR_OD14;
// SysTick enable with interupt and clk source to AHB/8
SysTick->CTRL = SysTick_CTRL_TICKINT_Msk | SysTick_CTRL_ENABLE_Msk;
SysTick->LOAD = 1000000; // 0.5 sec / (16 MHz / 8)
// Do forever:
while (1)
{
// Wait a moment
while (!flag)
{
__asm__(" WFI"); // sleep until SysTick
}
flag = false;
// Flip all LEDs
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD12
| GPIO_ODR_OD13
| GPIO_ODR_OD14
| GPIO_ODR_OD15;
}
}
assignment 3.5
Now based on project opdr_3_4 create a rotation loop which simulates a simple traffic light: green (5 seconds), orange (1 second), red (4 seconds). The time each light is on must be easily adjustable with a granularity of
0.5s. The processor must be put to sleep in between interrupts. Make use of an enumeration construct (enum) for the colors and aswitch-case-statement for the rotation.
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stm32f4xx.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
volatile bool flag = false;
void SysTick_Handler()
{
flag = true;
}
enum STATE {
STATE_GREEN,
STATE_ORANGE,
STATE_RED
};
int main(void)
{
// GPIO Port D Clock Enable
RCC->AHB1ENR = RCC_AHB1ENR_GPIODEN;
// GPIO Port D Pin 15 down to 12 Push/Pull Output
GPIOD->MODER = GPIO_MODER_MODER12_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER13_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER14_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER15_0;
// Set green and red LEDs
GPIOD->ODR = GPIO_ODR_OD12;
// SysTick enable with interupt and clk source to AHB/8
SysTick->CTRL = SysTick_CTRL_TICKINT_Msk | SysTick_CTRL_ENABLE_Msk;
SysTick->LOAD = 1000000; // 0.5 sec / (8 MHz / 8)
// time of each color in half seconds
const uint32_t time_green = 10; // 5 seconds
const uint32_t time_orange = 2; // 1 seconds
const uint32_t time_red = 8; // 4 seconds
uint32_t timer = time_green;
enum STATE State = STATE_GREEN;
// Do forever:
while (1)
{
// Wait a moment
while (!flag)
{
__asm__(" WFI"); // sleep until SysTick
}
flag = false;
timer--;
if (timer == 0)
{
// turn off all leds
GPIOD->ODR &= ~(GPIO_ODR_OD12
| GPIO_ODR_OD13
| GPIO_ODR_OD14
| GPIO_ODR_OD15);
switch (State) {
case STATE_GREEN:
State = STATE_ORANGE;
GPIOD->ODR |= GPIO_ODR_OD13;
timer = time_orange;
break;
case STATE_ORANGE:
State = STATE_RED;
GPIOD->ODR |= GPIO_ODR_OD14;
timer = time_red;
break;
case STATE_RED:
State = STATE_GREEN;
GPIOD->ODR |= GPIO_ODR_OD12;
timer = time_green;
break;
}
}
}
}
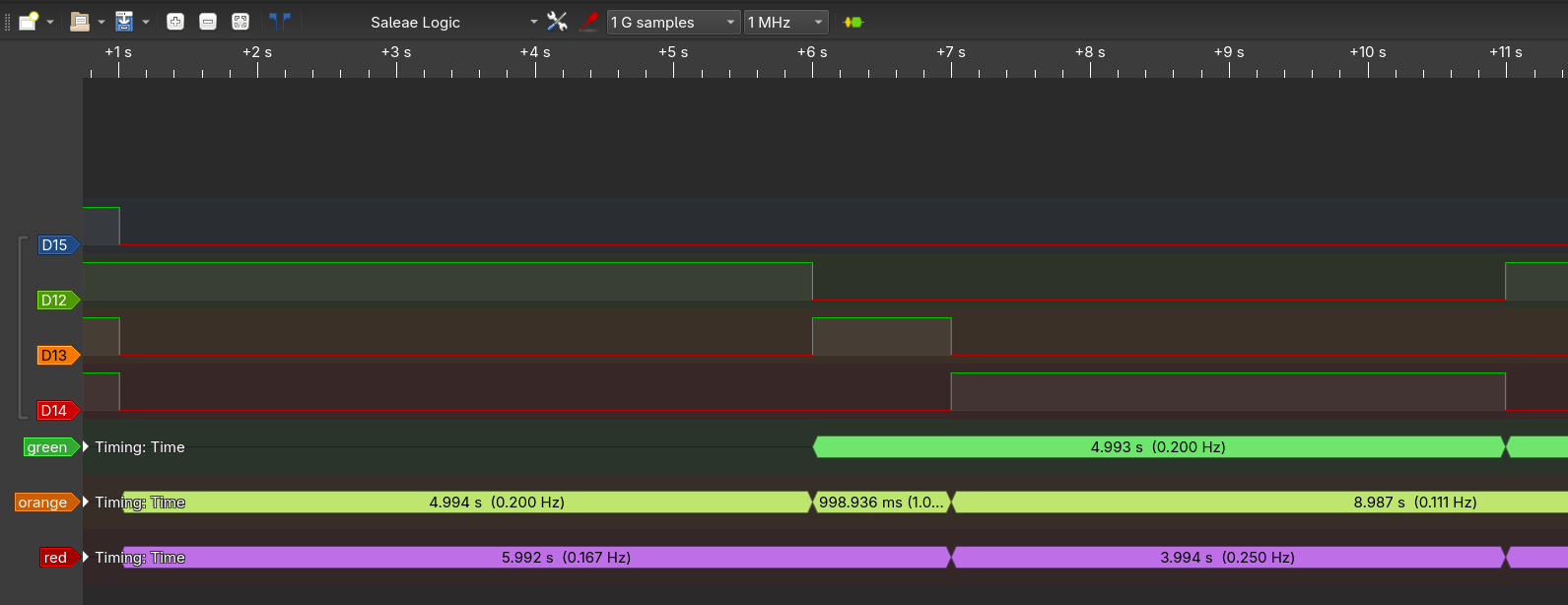
Again I validated the timesing with the logicanalyser.
assignment 3.6
- reate a copy of the previous project and rename it to opdr_3_6.
- Using the description of this assignment, define a struct for a “task” and create a global array of 8 empty tasks.
- Create a function
addTask(...)to help create a task from a function pointer and other parameters, and add it to the task list (the array) at an appropriate index.- Create 4 functions to toggle each led separately, these are the functions that will correspond to 4 tasks.
- Use
addTask(...)4 times to couple each led function to a new task in the task list with periods of: 200 ticks, 500 ticks, 750 ticks, and 300 ticks for green, orange, red, and blue respectively.- In the SysTick ISR, walk through the task list and decrement each of the task counters.
- Think of, and expand on, the task struct to notify per task whether it is in a WAITING or READY state. Set the state in the ISR depending on the task counter.
- Create a function runReadyTasks() that will walk through the task list and execute any task in the READY state. Replace your switch-case rotation in the function main with a call to this function.
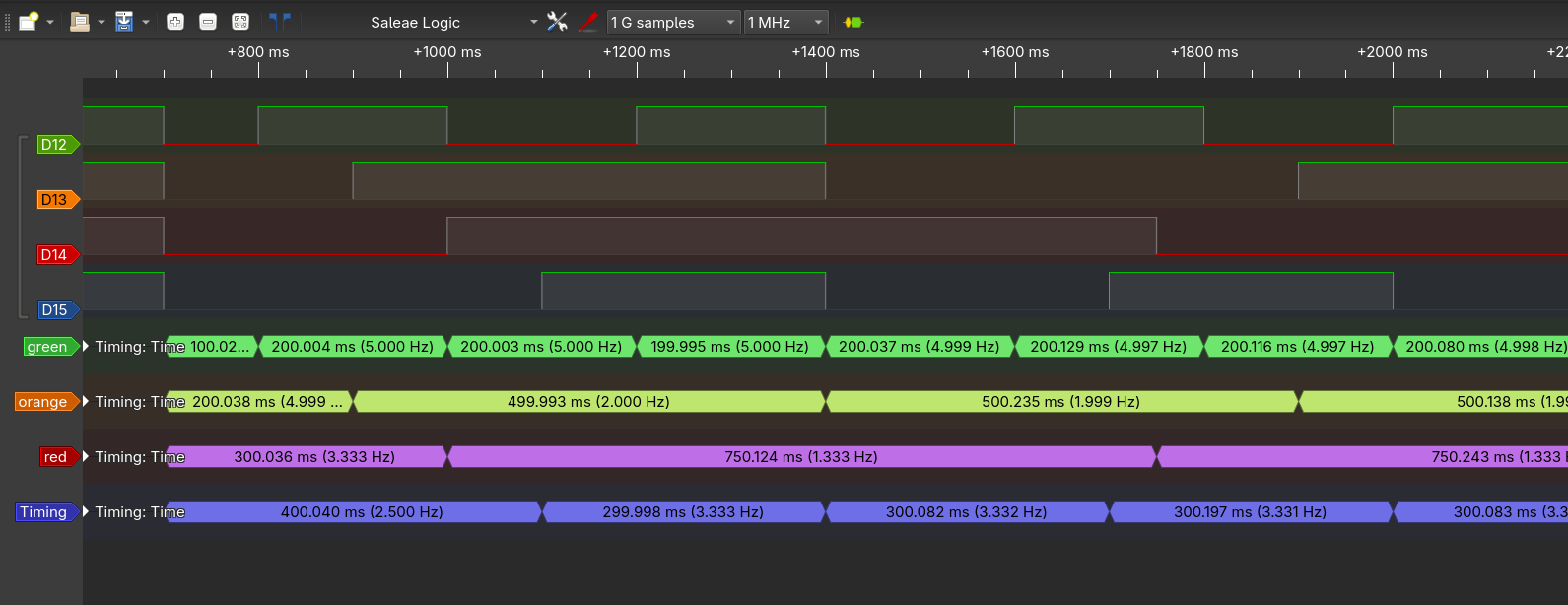
- Make use of a logic analyzer to verify the timing of the tasks
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stm32f4xx.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
volatile uint32_t ISR_Ticks = 0;
struct TASK {
void (*fn)(void);
uint32_t counter;
uint32_t counter_rst;
};
uint8_t Tasks_len = 0;
struct TASK Tasks[8];
void SysTick_Handler()
{
ISR_Ticks++;
}
bool addTask(void (*fn)(void), uint32_t counter)
{
if (Tasks_len >= 8) {
return false;
}
Tasks[Tasks_len].fn = fn;
Tasks[Tasks_len].counter = counter;
Tasks[Tasks_len].counter_rst = counter;
Tasks_len++;
return true;
}
void taskGreen()
{
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD12;
}
void taskOrange()
{
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD13;
}
void taskRed()
{
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD14;
}
void taskBlue()
{
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD15;
}
enum STATE {
STATE_GREEN,
STATE_ORANGE,
STATE_RED
};
int main(void)
{
// GPIO Port D Clock Enable
RCC->AHB1ENR = RCC_AHB1ENR_GPIODEN;
// GPIO Port D Pin 15 down to 12 Push/Pull Output
GPIOD->MODER = GPIO_MODER_MODER12_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER13_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER14_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER15_0;
// Set all leds off
GPIOD->ODR = 0;
// SysTick enable with interupt and clk source to AHB/8
SysTick->CTRL = SysTick_CTRL_TICKINT_Msk | SysTick_CTRL_ENABLE_Msk;
SysTick->LOAD = 2000; // 1 ms / (16 MHz / 8)
addTask(*taskGreen, 200);
addTask(*taskOrange, 500);
addTask(*taskRed, 750);
addTask(*taskBlue, 300);
// Do forever:
while (1)
{
// Wait a moment
while (ISR_Ticks == 0)
{
__asm__(" WFI"); // sleep until SysTick
}
uint32_t ticks = ISR_Ticks;
ISR_Ticks = 0;
// decrement all counters
for (uint8_t i=0; i<Tasks_len; i++)
{
if (Tasks[i].counter > ticks)
{
Tasks[i].counter -= ticks;
}
else
{
Tasks[i].counter = 0;
}
}
// rust all tasks where the counter has run out
for (uint8_t i=0; i<Tasks_len; i++)
{
if (Tasks[i].counter == 0)
{
Tasks[i].fn();
Tasks[i].counter = Tasks[i].counter_rst;
}
}
}
}
Assignment 3.7
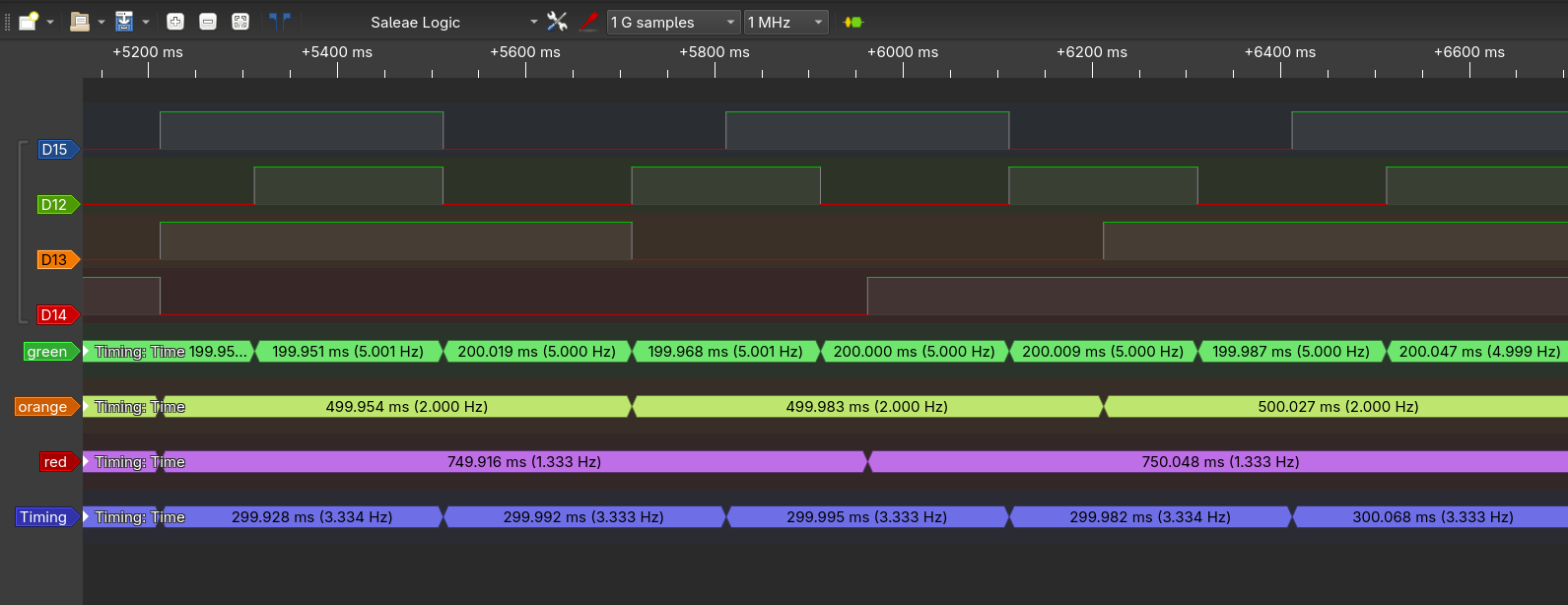
Now add initial delays5 (in systicks) to your tasks. Use an initial delay of 100, 200, 300, and 400 for green, orange, red, and blue respectively. Make use of a logic analyzer to verify the timing.
When A task is created, in the version of #Assignment 3.7, the folloing function is used:
bool addTask(void (*fn)(void), uint32_t counter)
{
if (Tasks_len >= 8) {
return false;
}
Tasks[Tasks_len].fn = fn;
Tasks[Tasks_len].counter = counter;
Tasks[Tasks_len].counter_rst = counter;
Tasks_len++;
return true;
}
Here the counter and counter_rst menbers are set to the same value. counter is the counter that is decremented eacht SysClock. counter_rst is the value counter is reset to if it reachts 0 after the task is run.
Setting counter to the initail delay already solves this assignment. The foloing code implements this change.
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stm32f4xx.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
volatile uint32_t ISR_Ticks = 0;
struct TASK {
void (*fn)(void);
uint32_t counter;
uint32_t counter_rst;
};
uint8_t Tasks_len = 0;
struct TASK Tasks[8];
void SysTick_Handler()
{
ISR_Ticks++;
}
bool addTask(void (*fn)(void), uint32_t counter, uint32_t counter_init)
{
if (Tasks_len >= 8) {
return false;
}
Tasks[Tasks_len].fn = fn;
Tasks[Tasks_len].counter = counter_init;
Tasks[Tasks_len].counter_rst = counter;
Tasks_len++;
return true;
}
void taskGreen()
{
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD12;
}
void taskOrange()
{
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD13;
}
void taskRed()
{
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD14;
}
void taskBlue()
{
GPIOD->ODR ^= GPIO_ODR_OD15;
}
enum STATE {
STATE_GREEN,
STATE_ORANGE,
STATE_RED
};
int main(void)
{
// GPIO Port D Clock Enable
RCC->AHB1ENR = RCC_AHB1ENR_GPIODEN;
// GPIO Port D Pin 15 down to 12 Push/Pull Output
GPIOD->MODER = GPIO_MODER_MODER12_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER13_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER14_0
| GPIO_MODER_MODER15_0;
// Set all leds off
GPIOD->ODR = 0;
// SysTick enable with interupt and clk source to AHB/8
SysTick->CTRL = SysTick_CTRL_TICKINT_Msk | SysTick_CTRL_ENABLE_Msk;
SysTick->LOAD = 2000; // 1 ms / (16 MHz / 8)
addTask(*taskGreen, 200, 100);
addTask(*taskOrange, 500, 200);
addTask(*taskRed, 750, 300);
addTask(*taskBlue, 300, 400);
// Do forever:
while (1)
{
// Wait a moment
while (ISR_Ticks == 0)
{
__asm__(" WFI"); // sleep until SysTick
}
uint32_t ticks = ISR_Ticks;
ISR_Ticks = 0;
// decrement all counters
for (uint8_t i=0; i<Tasks_len; i++)
{
if (Tasks[i].counter > ticks)
{
Tasks[i].counter -= ticks;
}
else
{
Tasks[i].counter = 0;
}
}
// rust all tasks where the counter has run out
for (uint8_t i=0; i<Tasks_len; i++)
{
if (Tasks[i].counter == 0)
{
Tasks[i].fn();
Tasks[i].counter = Tasks[i].counter_rst;
}
}
}
}